Sleep is a fascinating and essential aspect of our lives. It’s a time when our bodies and minds rejuvenate, repair, and prepare for the challenges of the day ahead. But have you ever wondered what happens to your body during sleep? How does it affect your overall health and well-being?
In this article, we will delve into the science of sleep, exploring the intricacies of sleep cycles and their impact on our physical and mental health.
Why Sleep Matters
Before we dive into the details of sleep cycles, let’s take a moment to understand why sleep matters. Sleep is not merely a state of rest; it plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. When we sleep, our bodies undergo a series of complex processes that contribute to various aspects of our physical and mental functioning.
The Sleep Cycle: An Intricate Dance
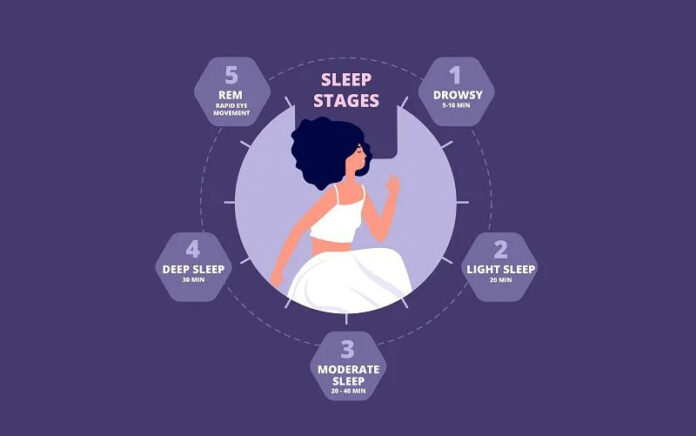
Sleep is composed of several cycles, each consisting of distinct stages. These cycles repeat throughout the night, with each cycle lasting approximately 90 minutes. During a typical night’s sleep, we go through four to six complete sleep cycles.
Stage 1: Transition to Sleep
The first stage of sleep is a transitional phase between wakefulness and sleep. During this stage, we may experience drifting thoughts and fleeting sensations. It is relatively easy to be awakened during this stage, and it usually lasts for about 5 to 10 minutes.
Stage 2: Light Sleep
Stage 2 is the first true stage of sleep. Our brain waves slow down, and our body temperature begins to drop. This stage accounts for a significant portion of our sleep and plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. It is during this stage that our brain processes and organizes information gathered throughout the day.
Stage 3: Deep Sleep
Stage 3 is also known as slow-wave sleep or deep sleep. During this stage, our brain waves slow down even further, and our muscles relax. Deep sleep is essential for physical restoration, as it promotes tissue repair, muscle growth, and the release of growth hormones. It is also believed to be crucial for immune function and overall well-being.
REM Sleep: The Dream Stage
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is perhaps the most intriguing stage of sleep. It is associated with vivid dreaming and rapid eye movements. During REM sleep, our brain activity increases, similar to when we are awake. This stage is crucial for learning, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation. It is also believed to be linked to creativity and problem-solving.
The Sleep Cycle Repeats
After the REM stage, the sleep cycle starts over again, beginning with stage 1. As the night progresses, the amount of time spent in REM sleep increases, while deep sleep decreases. This pattern is known as the ultradian rhythm, a recurring cycle that repeats multiple times during a single night of sleep.
The Impact of Sleep Deprivation
Now that we have a basic understanding of sleep cycles, let’s explore the consequences of sleep deprivation. Sleep deprivation occurs when we consistently fail to get enough sleep to meet our body’s needs. It can have profound effects on our physical and mental health.
Lack of sleep affects our cognitive functioning, impairing our attention, concentration, and decision-making abilities. It also weakens our immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and diseases. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of conditions such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and even certain types of cancer.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on our physical and mental well-being. When we consistently fail to get enough sleep, our bodies and minds suffer. Here are some common symptoms of sleep deprivation:
- Daytime Sleepiness: Feeling excessively tired and struggling to stay awake during the day is a hallmark symptom of sleep deprivation. Despite efforts to stay alert, individuals may experience frequent episodes of drowsiness and a strong desire to nap.
- Poor Concentration and Memory: Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive function, making it challenging to concentrate, focus, and retain information. It becomes harder to stay attentive during tasks, leading to decreased productivity and performance.
- Mood Changes: Lack of sleep can significantly impact our mood and emotional well-being. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience irritability, mood swings, increased sensitivity, and a higher likelihood of experiencing negative emotions such as sadness or frustration.
- Weakened Immune System: Sleep plays a crucial role in supporting our immune system. When we don’t get enough rest, our body’s ability to fight off infections and illnesses diminishes. Sleep deprivation can make us more susceptible to colds, flu, and other infections.
- Increased Hunger and Weight Gain: Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of hormones that regulate appetite, leading to an increase in hunger and cravings, particularly for high-calorie and sugary foods. This can contribute to weight gain and difficulties in maintaining a healthy diet.
- Impaired Motor Skills: Lack of sleep affects coordination and motor skills, making simple tasks that require precision, such as driving or operating machinery, more dangerous. Reaction times may be slower, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Reduced Libido: Sleep deprivation can negatively impact our sex drive and overall sexual function. Fatigue and hormonal imbalances caused by lack of sleep may lead to a decrease in sexual desire and performance.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions: Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of developing serious health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Tips for Better Sleep
Given the importance of sleep, it’s crucial to prioritize healthy sleep habits. Here are some tips to help you improve the quality and duration of your sleep:
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillow that support your body’s needs.
- Establish a bedtime routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
- Limit exposure to screens: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your sleep. Avoid using screens for at least an hour before bedtime.
- Avoid stimulants: Limit your consumption of caffeine and nicotine, especially in the evening. These substances can disrupt your sleep patterns.
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in physical activity during the day can help promote better sleep at night. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it may make it harder for you to fall asleep.
- Manage stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing mindfulness meditation, journaling, or talking to a trusted friend or therapist.
Establishing a Healthy Sleep Routine
Creating a healthy sleep routine is crucial for ensuring quality sleep and optimizing your overall well-being. Here are some tips to help you establish a routine that promotes restful and rejuvenating sleep:
- Set a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes a regular sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make your bedroom a comfortable and inviting space for sleep. Ensure that your room is cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out any disturbances.
- Develop a Bedtime Routine: Establish a relaxing routine before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, practicing gentle stretches, or listening to calming music.
- Limit Exposure to Screens: The blue light emitted by electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, can interfere with your sleep. Avoid using screens for at least an hour before bedtime. Instead, engage in screen-free activities that promote relaxation.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit your consumption of caffeine and nicotine, especially in the evening. These substances are stimulants that can disrupt your sleep patterns. Opt for herbal tea or decaffeinated alternatives instead.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity during the day can promote better sleep at night. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it may make it harder for you to fall asleep.
- Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can interfere with sleep. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation, or yoga), journaling, or engaging in a calming hobby. If necessary, seek support from a therapist or counselor.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Bedtime Environment: Make your bed a sanctuary for sleep. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that support your body’s needs. Consider using breathable bedding and ensuring that your bedroom is at a temperature conducive to sleep.
- Avoid Daytime Napping: If you’re struggling with sleep at night, try to avoid daytime napping, especially in the late afternoon or evening. If you must nap, keep it short (around 20-30 minutes) and earlier in the day.
- Limit Liquid Intake Before Bed: To prevent disruptions from frequent bathroom trips during the night, limit your liquid intake in the hours leading up to bedtime. However, make sure you stay adequately hydrated throughout the day.
Conclusion
Sleep is a fascinating and essential aspect of our lives. Understanding the science of sleep, including sleep cycles and their impact on our health, is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. By prioritizing healthy sleep habits and ensuring we get enough rest each night, we can optimize our physical and mental functioning, enhance our productivity, and improve our overall quality of life.
Remember, a good night’s sleep is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. So, take the time to create a sleep-friendly environment, establish a consistent bedtime routine, and prioritize self-care. Your body and mind will thank you for it.
Sweet dreams!







